Call Now: (+61) 416-195-006
Part 1
The bonds are determined by market forces both globally and locally, and we have a variety of marketplaces like Bloomberg users, Yieldbroker debts, and tradeweb. Australian commonwealth government securities offer 3 types of securities, and these are:
- treasury notes.
- treasury bonds.
- treasury indexed bonds.
Both interest rates and bond yields have been decreasing since long time. Like when COVID 19 crisis breaks out, the bond’s rate of decline accelerated, making it a favourable investment. The Australian commonwealth government securities comprise commodities that provide assurance to various funds including superannuation funds in the situation of stress and doubts, and further the rates decline, the higher the amount of the securities.
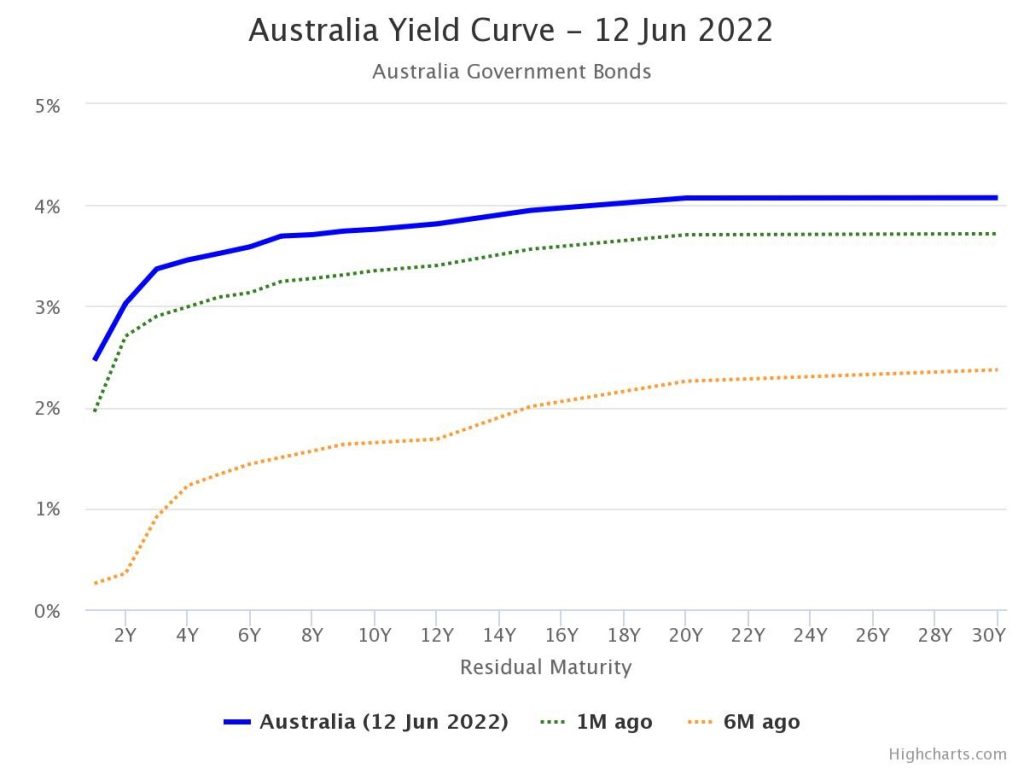
As the situation became more convoluted in February 2020 as a result of COVID-19, it became clear that this scenario is having a detrimental influence on global economies. The value of risky assets, like stocks, has dropped. Risk-free assets are becoming less popular. Bonds that are risk-free and generally released by the government and are highly rated have fallen in prices over time during periods of heightened economic uncertainty, and the same has happened following the crisis of COVID-19 worries. When compared to March, the yields on Australian Commonwealth government securities have fallen to very low levels. This pattern has been similar in other regions as well.
Nevertheless, the normal decrease in government bond yield owing to price hike in reaction to declining of the economic outlook resulted in an unsuspected abrupt increase in yields caused by price cutting. The decline in asset values, along with increased uncertainty about the underlying economic circumstances, resulted in a severe spike in turbulence, as a huge assortment of investors wanted cash to satisfy margin requirements, limit leverage, and satisfy withdrawal. Because government bonds were very liquid, a huge group of shareholders opted to sell them. Unlike many other asset types, securities owned by government may be sold in huge numbers irrespective of its negative impact on the market.
Bond dealers primarily acquired government bonds, but their aim to engage in more transactions and help the price investigation process worsened when their own balance sheets started to exceed statutory and internal risk restrictions, resulting in rising instability and reduced liquidity. AGS’s capacity to interact was impeded by work-from-home settings, which reduced trading activity and resulted in a steady reduction in total yield. Bond prices decease in relation to future prices, which we had a better chance of seeing expressed in the bond market's substantially higher bid-offer spreads and weaker liquidity. Investors expected to profit from the leveraged process, but the reverse occurred, resulting in huge mark-to-market losses. Some investors were obliged to reverse their positions and either satisfy internal risk limitations or satisfy margin calls, placing more emphasis on an already unstable market and creating a greater spiral basis where higher basis led to higher basis.
The risk of rolling and securing repo funding, which is compounded by investors to reap the benefits of arbitrage possibilities, is one of the reasons. Second, because we have an unsatisfactory hedge for the futures in the underpinning bonds, even the most well and secured deal may not even be risk-free.
Implications for Fixed-Interest fund managers
Locally and internationally portfolio managers who had margin calls and redemption demands to satisfy. Several investors used enormous leverage to sell the bonds, with the goal of making as much profit as possible. Investor sales entailed deals between bonds and futures contracts that were hedged against or faced margin calls due to increasing uncertainty. The increasing uncertainty surrounding the issue of future government bonds may have led to a spike in yields and fluctuations.
Interest Rates in Australia
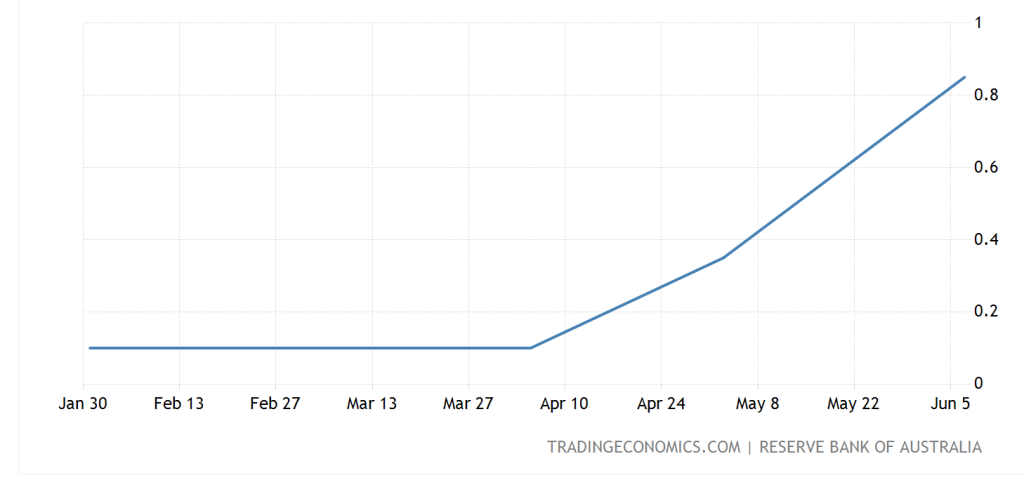
6-month:
The projection for Australia's gdp seems "good," with growth of 4.25 percent in 2022 and 2 percent the following year. But, there are risks to the international economy, including as the Russia-Ukraine conflict and China's Covid problems. Over the course of the month, the domestic yield curve rose and flattened. The three-year government bond yield jumped 37 basis points (bps) to 2.71 percent as increasing prospects were moved forward. Yields rose at the longer end of the yield curve as well, albeit not to the same amount. The rates on 10-year and 30-year government bonds increased by 29 basis points and 21 basis points, respectively, to conclude the month at 3.13 percent and 3.46 percent.
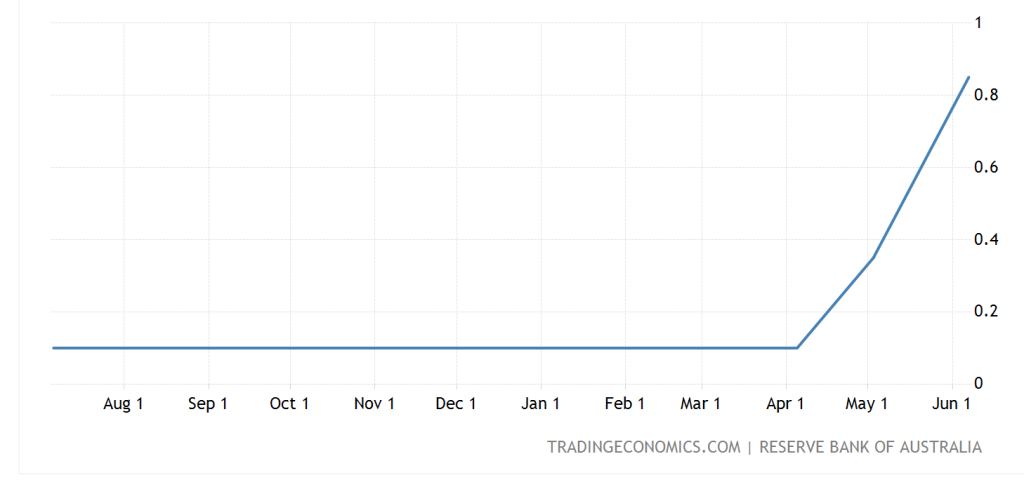
12-month:
In response to rising consumer costs, Australia raised its interest rate for the first time in more than a decade. According to the consensus expectation of 32 economists polled by Reuters, the increase was higher than the expert estimate of 15 basis points to 0.25 percent. In March, the rate of job growth slowed, with a 17,900 increase in employment falling short of market forecasts. The jobless rate increased to 4.0 percent from 3.9 percent previously. Forward-looking labour market indicators indicate that the labour market will remain strong in the foreseeable future. The turn to an early start to a big tightening cycle continues to be reflected in the short-term financial markets.
B ) Bond rates are projected to be equal to those predicted by an assumed zero-coupon yield curve in a stable market. If the case is opposite of this, it means that equivalent payments were evaluated through some other methods using other bonds, which we advise to decrease. If difference between observed yields and those with zero coupon yield are big then this would indicate price fluctuations of bonds, thus it shows weakness of the market players as they are not taking advantage of arbitrage possibilities related to price movements and employing trade to reduce price fluctuations.

Chat with our Experts
Want to contact us directly? No Problem. We are always here for you
